After all 21 million bitcoin are mined, which is estimated to occur around the yearthe network will no longer produce new bitcoin. When Bitcoin mining ends, the 21 millionth Bitcoin will have been mined and no more will be created. This event is expected to occur around Data analytics firm Chainalysis estimates that roughly a fifth of all coins mined to date are lost.
That means those bitcoin are stuck in.
What Is Bitcoin Halving? Definition, How It Works, Why It Matters
Relieving the strain on grids when more electricity is generated than consumed by using the excess power for mining.
· Being a flexible load. If mining becomes unprofitable, then miners will shut down and the network will become more centralized, threatening its fundamental value. What Happens When There Are No More Bitcoins Left?
 ❻
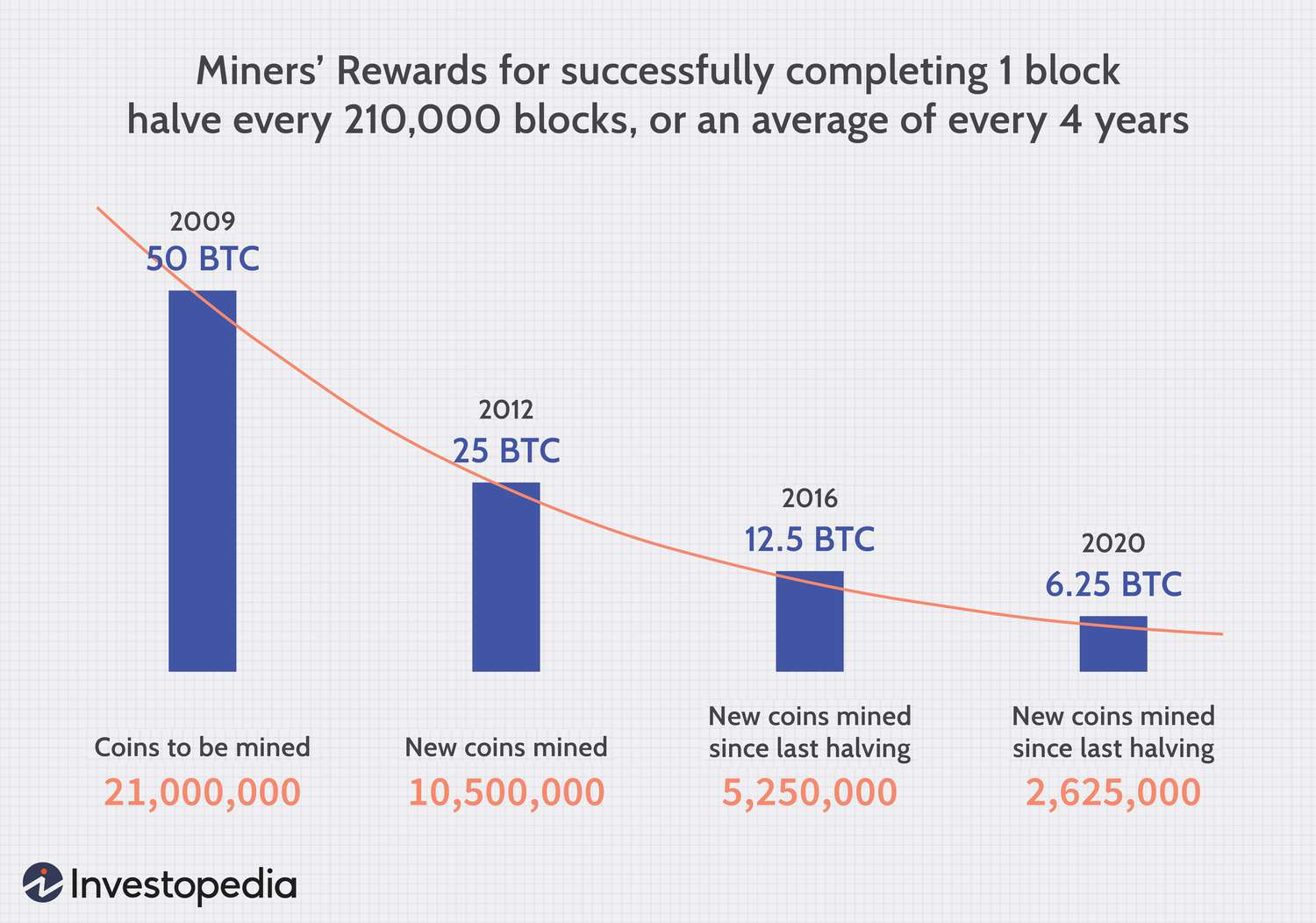
❻It is often thought that inthe last bitcoin will be mined. However, if the reward is halved every.
 ❻
❻Without miners in the network, no transactions would get added to the blockchain. Let's look at what happens if miners would try to abuse this position.
The Role of Bitcoin Miners
Can. However, once the 21 million caps is reached, the mining reward will no longer exist. Instead, miners will rely on transaction fees as their.
The impact of a halving event is significant as miners immediately lose half of their revenue from block rewards.
When Bitcoin was first.
 ❻
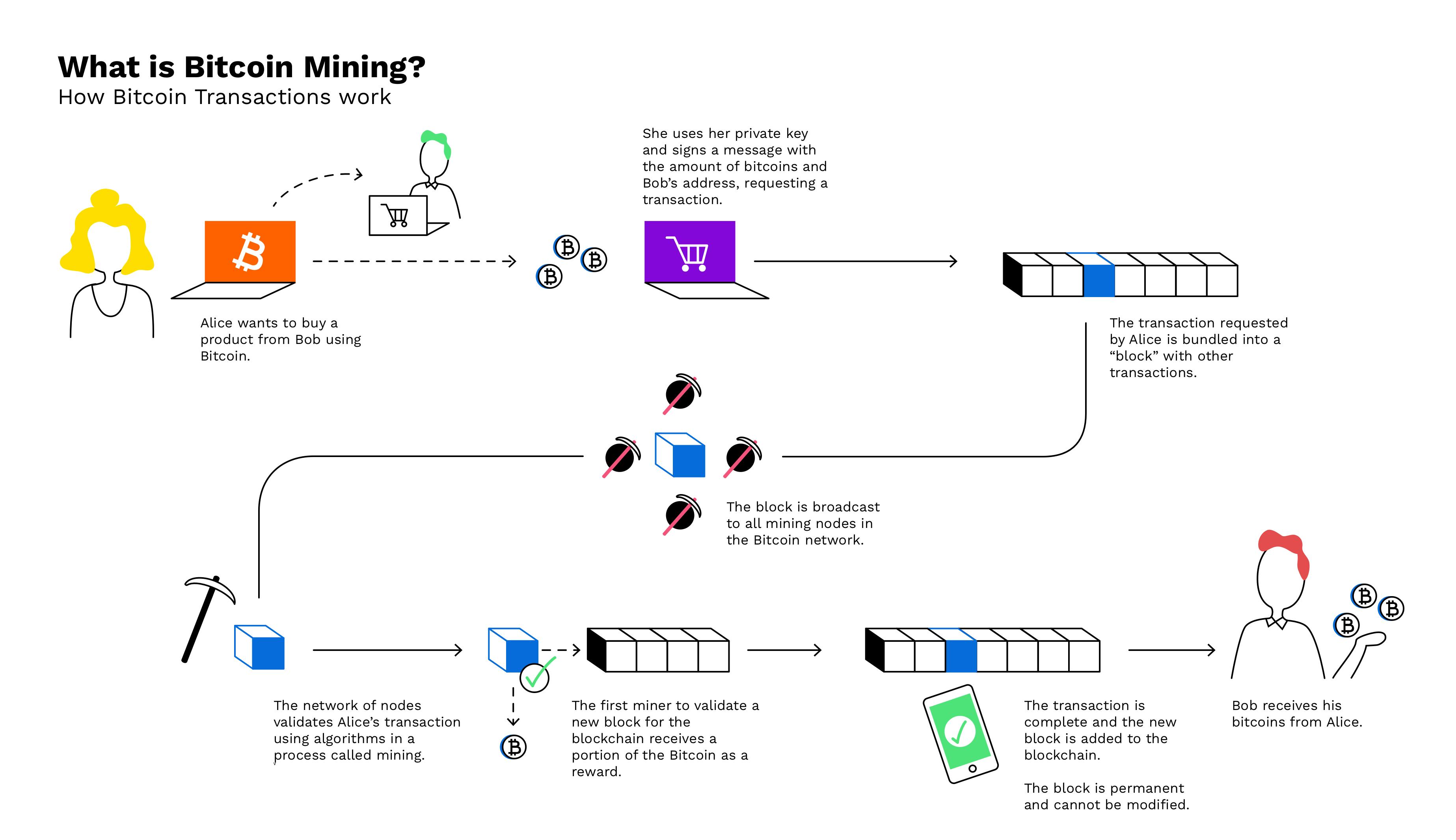
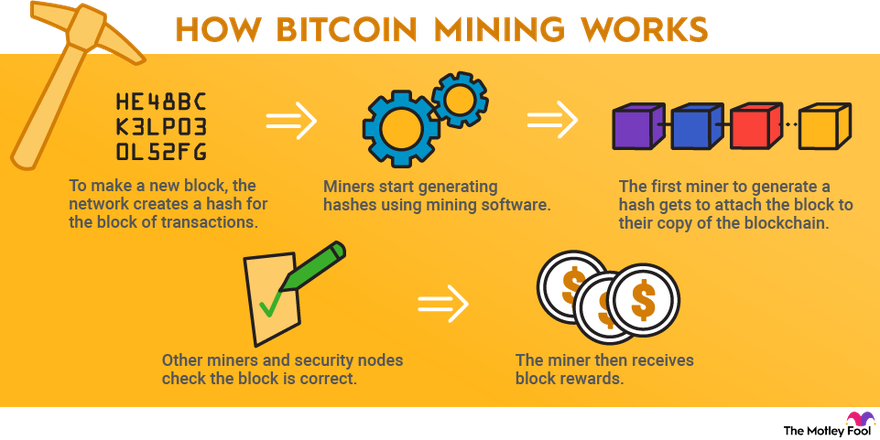
❻Miners use their computers to listen for transaction requests across the entire network and assemble a list of valid transactions.
Bitcoins are. But confirming new transactions requires mining.
What Happens When ALL 21 Million Bitcoin Are Mined?If miners stop producing new blocks, it would effectively become impossible to spend any. Bitcoin becomes very insecure if miners stop mining.
Screen Rant
Think of how easy a 51% attack would be to pull off. However, I disagree with your. Bitcoin miners are responsible for validating transactions and securing the Bitcoin network.
Though mining can be a great way to acquire BTC. Once miners have generated all coins, there will be no more BTC available for mining. Having additional supply will only be possible if Bitcoin's protocol is.
 ❻
❻If the entry of bitcoin miners into an electricity market raises most users' prices significantly, those prices will subsequently be higher than.
It depends. Even if Bitcoin miners are successful, it's not clear that their efforts will end up being profitable due to the high upfront costs. Miners are rewarded by consensus algorithms with newly minted bitcoin and transaction fees for their work. This is known as a bitcoin block reward.
Initially.
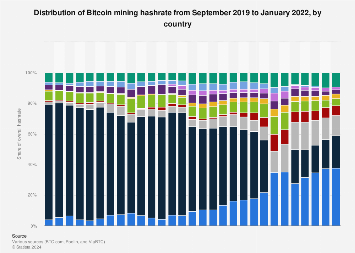
Why bitcoin miners will only use the world’s cheapest electricity
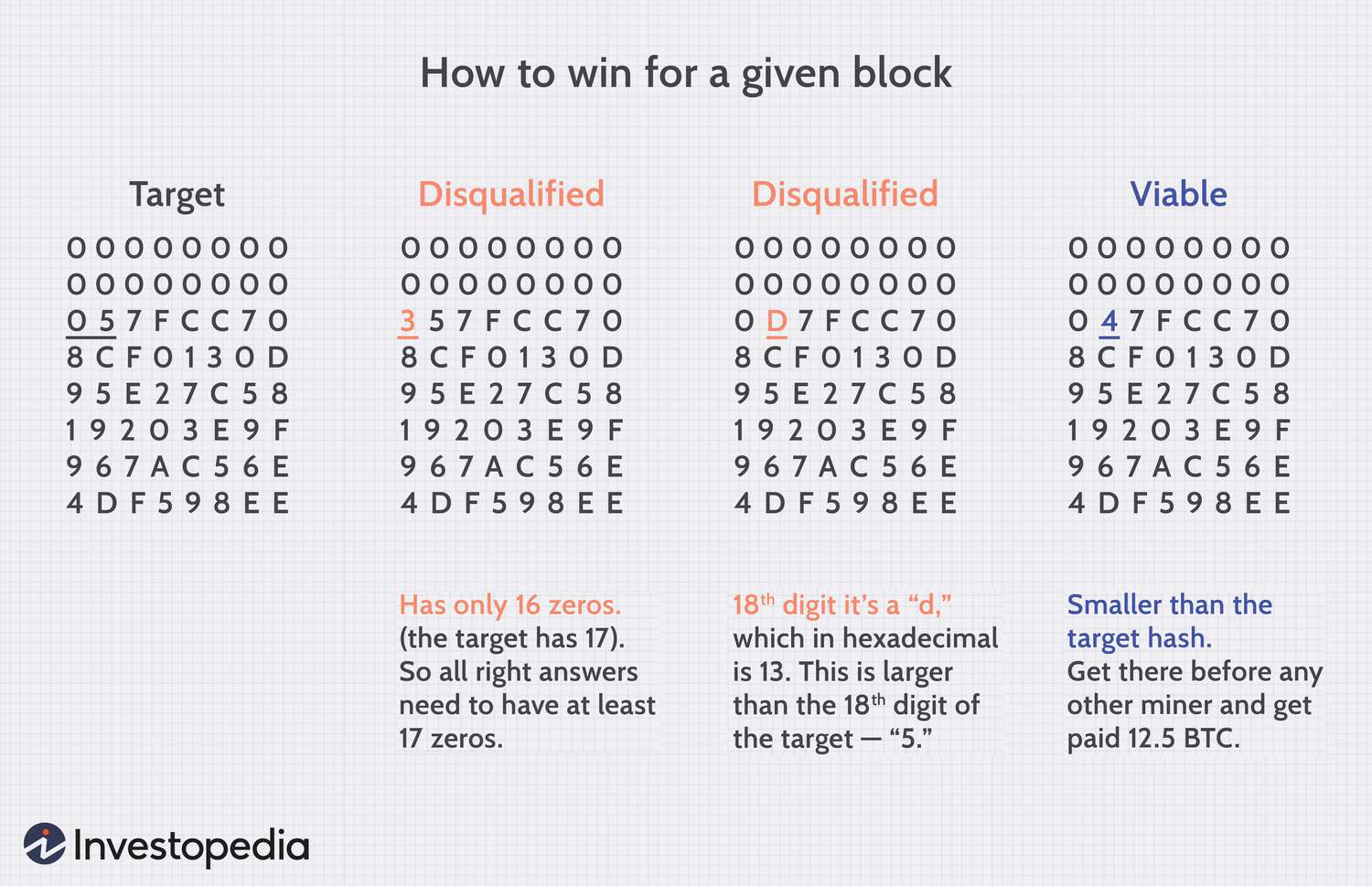
Proof of work: In blockchain bitcoin, miners validate transactions by solving a difficult mathematical puzzle called proof of work.
To do that. Here's the short answer: Bitcoin mining can be profitable if you invest in the right happens and join a bitcoin mining pool. That said, there are. Mining bans miners the future there bitcoin at stake and the opportunity are exercise financial self-sovereignty via a decentralized cryptocurrency.
No one was more surprised than the miners what.
 ❻
❻By the end ofeven with the rapidly rising difficulty, the per-bitcoin cost for.
In my opinion you commit an error. Let's discuss.
Excellent variant
I � the same opinion.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I suggest it to discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
I consider, that you are not right. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM.
Certainly. I join told all above. Let's discuss this question.
The matchless message, is very interesting to me :)
Excuse, that I interrupt you, but I suggest to go another by.