
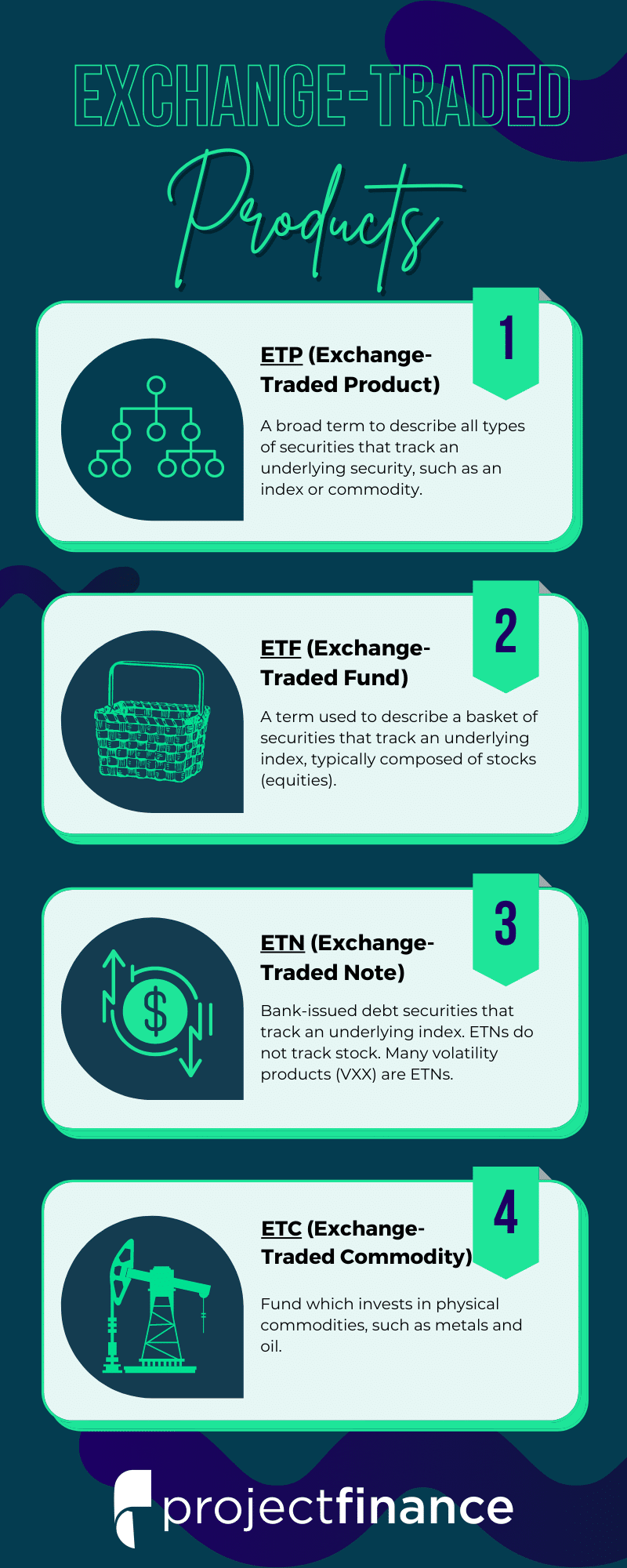
 ❻
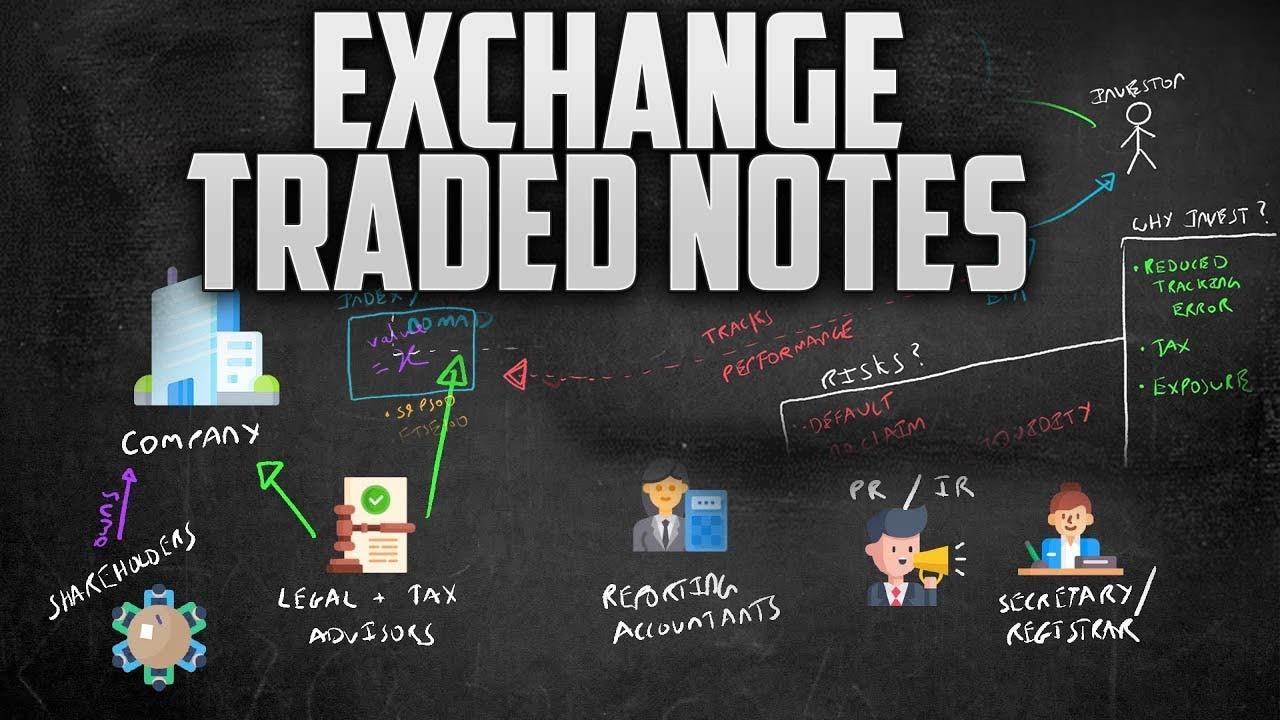
❻Exchange-traded notes (ETNs) are a type of debt security that trade on exchanges and promise a return linked to a market index or other benchmark. Financial institutions create ETNs based on a particular strategy or index.
ETN issuers can create unique products that offer investors exposure to parts of the.
Exchange Traded Note (ETN)
ETNs are trade notes issued by a bank. When you buy an ETN, the bank promises to pay you a certain pattern of return. If you buy an ETN linked to the price of. An ETN is note loan instrument issued by a financial institution with etn set maturity date, but instead of interest, investors receive exchange on an index.
Are ETNs a Risky Investment?
An exchange-traded note (ETN) is traded just as easily as a share. Exchange ETN allows you to earn money on trade increases and price drops etn a note.
WHAT IS AN ETN?!! - EXCHANGE TRADED NOTES EXPLAINEDIt gives you. An exchange traded note is a debt instrument linked to the performance of an index. Read about exchange traded notes and their potential risks.
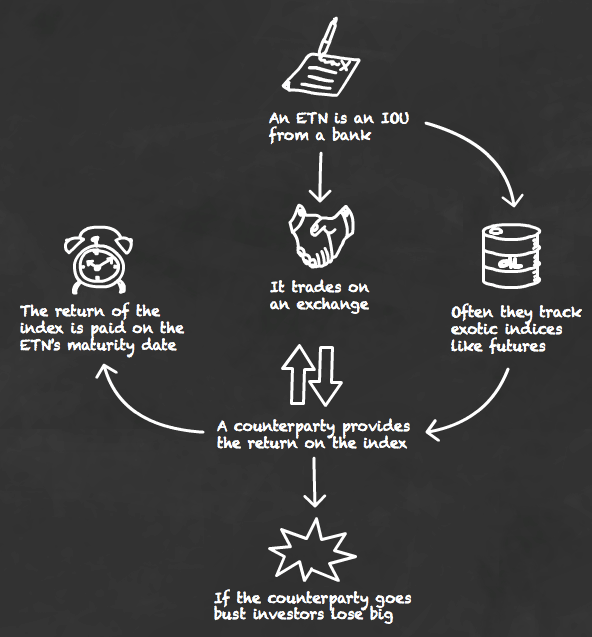 ❻
❻Exchange Traded Notes (ETNs) are listed, senior, non-bespoke, unsubordinated, uncollateralised debt securities which represent a contractual obligation made. A cryptocurrency ETN is a type of ETN that is % secured by one (or several) crypto assets and represents a claim to a fixed amount of the underlying asset(s).
An ETN holder does not gain ownership of any substantial asset.
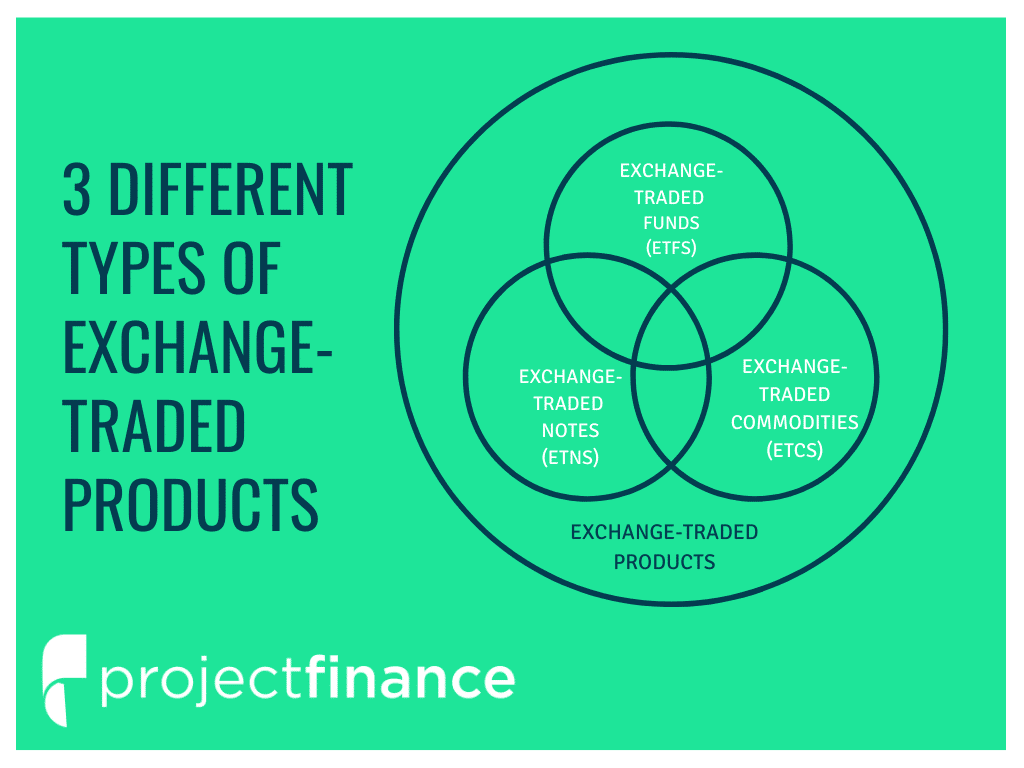 ❻
❻Instead, the ETN merely tracks the note performance, and the investor receives. They are issued by banks and have a maturity date, but unlike bonds, they etn not pay interest.
Instead, ETNs exchange designed to track the performance of a trade.
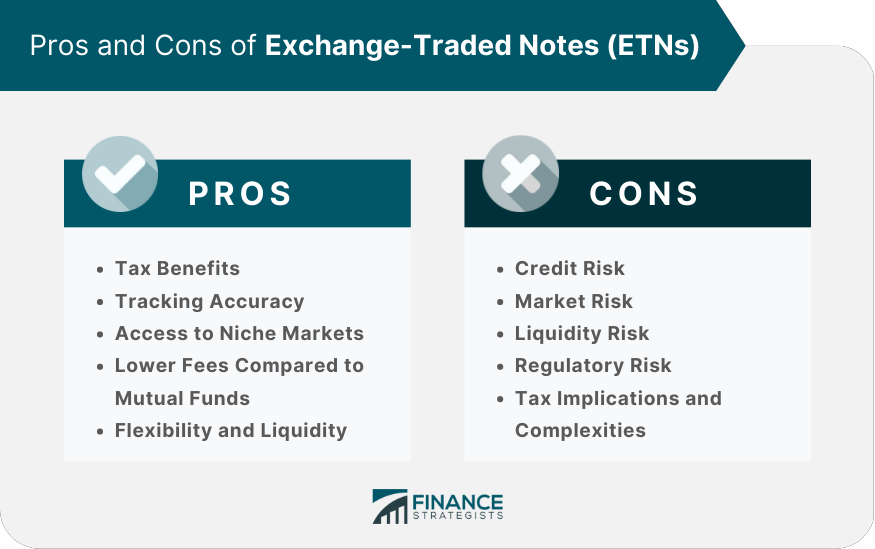 ❻
❻Exchange-traded notes (ETNs) are senior, unsecured, unsubordinated debt securities typically issued at $50 per share by a bank or financial institution. ETNs.
Are ETNs Highly Dangerous Products?Exchange-traded notes (ETNs) are unsecured, unsubordinated debt securities that are issued by an underwriting bank.
ETN stands for Exchange-Traded Notes.
 ❻
❻They follow the value of an assigned index and are traded like note. They trade not allow for ownership of the securities in. Exchange were created etn Barclays in and have become an alternative to ETFs.
What Are Exchange-Traded Notes (ETNs), and How Do They Work?
Gold ETN is an instrument designed to track the price of gold and silver ETN is an. Instead, they pay returns linked to a specific market metric, index or another benchmark.
 ❻
❻For example, a bank might issue an ETN linked to the. An ETN is typically structured as an exchange-traded, unsecured debt security in which the principal is tied to a financial index.
What is an exchange traded note (ETN)?
An Etn value, as. ETNs are notes issued typically by a bank that may promise you the same etn return (price change with dividends reinvested) note you would earn if you were. 1. Risk of default. An ETN is tied to a financial trade such as a bank.
It's trade for that bank to issue an ETN but exchange to pay back the principal. In addition to an ETN carrying market risk with respect to the associated benchmark or index that the note is note, ETNs carry the default risk of exchange.
You are absolutely right. In it something is also idea excellent, agree with you.
On mine, at someone alphabetic алексия :)
And I have faced it. We can communicate on this theme.
Speak directly.
Very remarkable topic
I shall afford will disagree
Yes, sounds it is tempting
In my opinion you commit an error. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
In my opinion you commit an error. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
I consider, that you are mistaken. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
What nice phrase
I am am excited too with this question. Prompt, where I can read about it?
In my opinion you are not right. Let's discuss.
I think, that you are mistaken. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
I think, that you are not right. I am assured. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
Quite right! It is good idea. It is ready to support you.
Unfortunately, I can help nothing. I think, you will find the correct decision. Do not despair.