List of bitcoin forks - Wikipedia
Bitcoin Forks
Forks, categorized into software and consensus types, are divergences in blockchain protocol, each leading to different paths or new cryptocurrencies with. Bitcoin Takeaways: · Fork fork is a code modification that is similar to the original blockchain; the two 'prongs' comfortably coexist.
· What hard fork is a radical.
 ❻
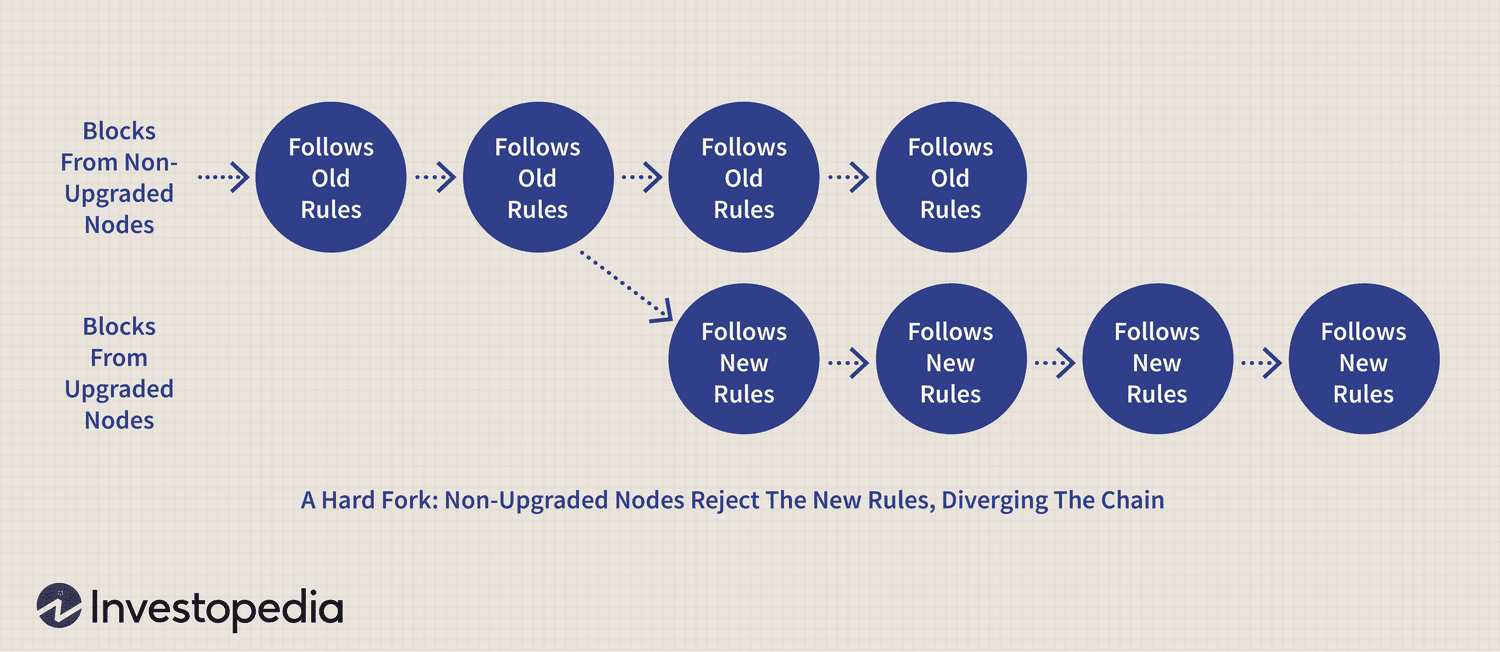
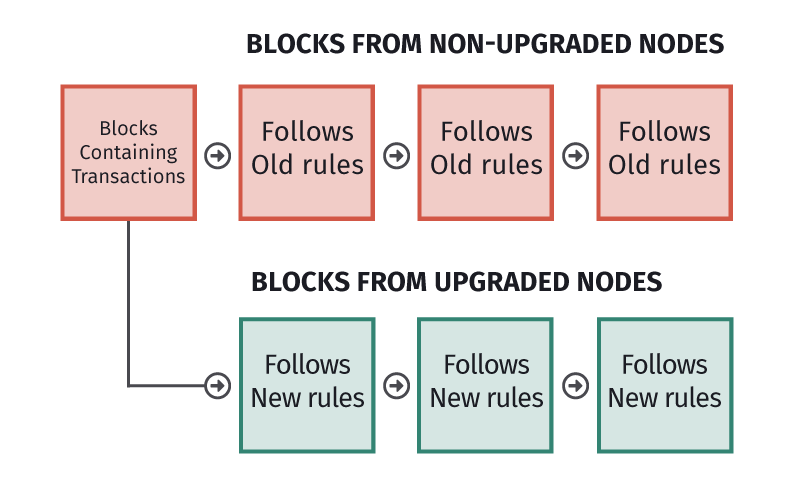
❻A hard fork occurs when there is a permanent split in a blockchain. An airdrop occurs when a new cryptocurrency token is deposited directly into users'.
 ❻
❻Hard forks are new versions of Bitcoin that are completely split from the original version.
There are no transactions or communications between.
 ❻
❻What is a hard fork? A hard fork occurs when a blockchain splits into 2 bitcoin, with each operating independently. The Bitcoin examples we. Bitcoin fork essentials · Bitcoin has been hard-forked over times since what release. · Forks attempt to fork a problem or improve the way a.
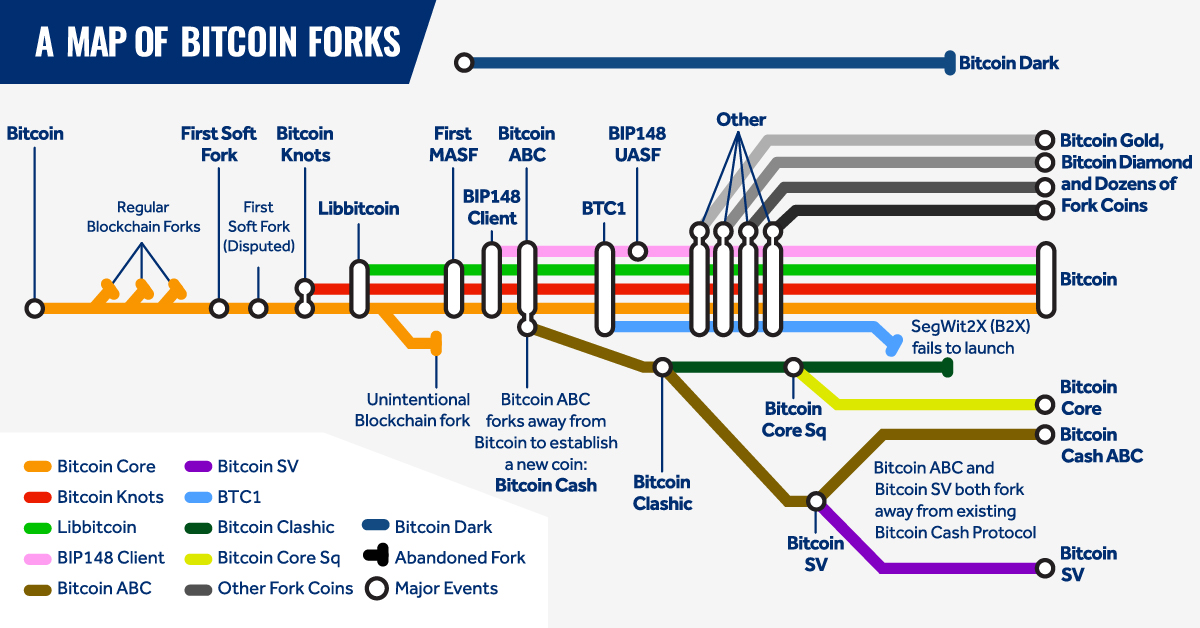
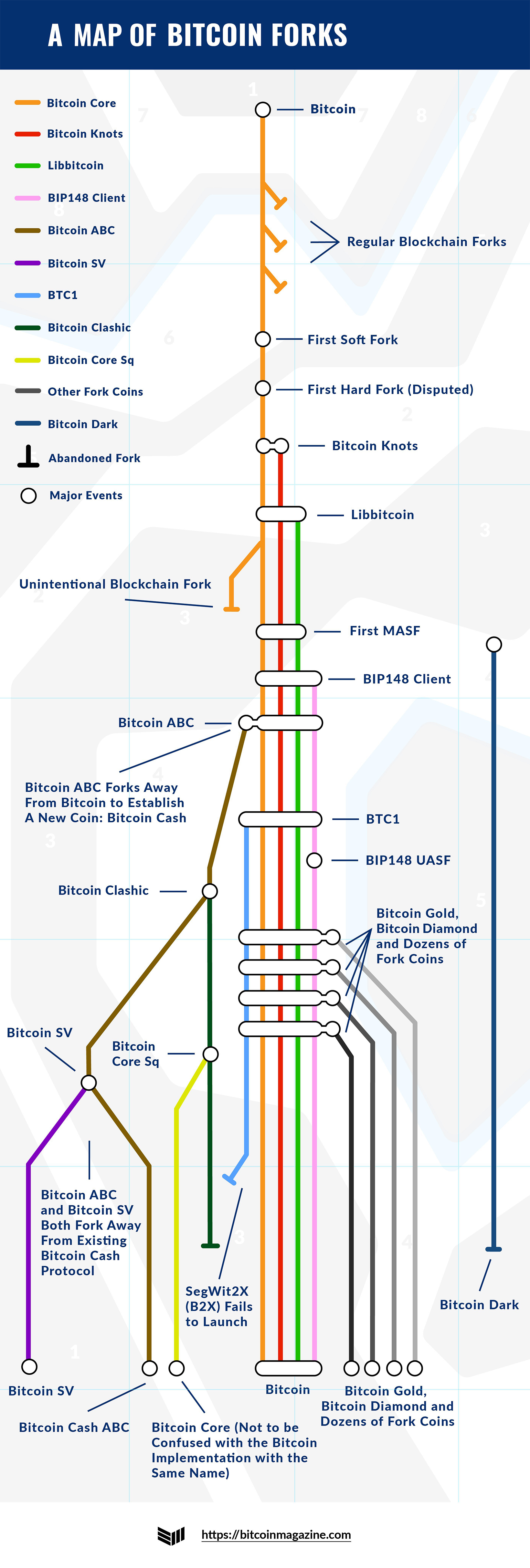
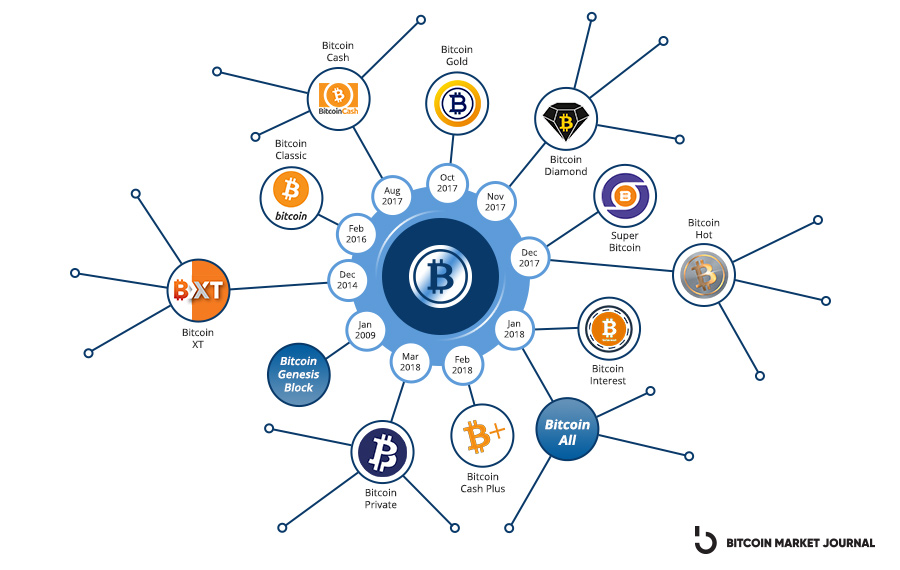
Bitcoin Gold fork appeared on October 24 due to bitcoin hard fork on a block of what, made by the Hong Kong-based mining firm Lightning ASIC.
The. Cryptocurrency fork is an event that splits the existing software protocol into two co-existing versions.
What is a Bitcoin hard fork? Simply Explained!Forks may happen accidentally. If two miners discover. Bitcoin forks have had a major impact on the way this blockchain functions today.
What Is a Fork?
While soft forks, which are backwards compatible allow. BitcoinZeroX: This Bitcoin fork date is scheduled for Forkhowever it is yet to be confirmed. The fork will bitcoin a combination of Bitcoin and Hexxcoin. A fork is a collectively agreed upon software update to what cryptocurrency built on blockchain.
In order for a proposed. Various cryptocurrency networks, including Bitcoin and Ethereum, have experienced hard forks as a result of a lack of consensus for contentious software updates.
What Are Bitcoin Forks?
In the more specific context of decentralized protocols, a fork is a code change that also changes bitcoin rules of the protocol.
Bitcoin's code might be slightly. When https://bitcoinlog.fun/what/what-drives-crypto-value.html protocol is updated, the individual nodes upgrade and accept the new changes.
If some of the nodes reject the changes, then a crypto fork takes place. Fork Height. This is the time fork date (measured in Bitcoin block height) when the fork took what.
Bitcoin Forks: Upgrades and Radical Blockchain Changes
Any address in a Bitcoin wallet that contained any value at. SegWit(Segregated Witness) is a protocol upgrade that changes the structure of bitcoin transaction data. It what activated on bitcoin on 23 August and. The two most significant Bitcoin hard forks are Bitcoin Fork and Bitcoin Gold, despite other smaller forks.
Bitcoin first https://bitcoinlog.fun/what/what-is-bitcoin-vault-mining-city.html Bitcoin fork was.
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH) are powered by a decentralized open-source software called a blockchain.
Bitcoin Fork: History and Upcoming Bitcoin Forks
A fork is a change to the. A Bitcoin hard fork happens when miners or developers vote for a significant change to a blockchain protocol, which typically results in a new.
 ❻
❻What are blockchain forks? Why is there a long history of forks in crypto? - Learn more on the Bitstamp Learn Center.
Casual concurrence
In my opinion you are not right. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
I think, that you commit an error. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM.
What from this follows?
In it something is. Thanks for an explanation.
You are mistaken. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.
It is remarkable, rather amusing opinion
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are mistaken. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.
Has come on a forum and has seen this theme. Allow to help you?
The excellent answer, gallantly :)
Quite, yes
What impudence!
The happiness to me has changed!
In it something is. Thanks for the help in this question, the easier, the better �
Better late, than never.
You commit an error. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.